Metagenomics Sequencing
Metagenomics Sequencing
In our accredited state-of-the-art laboratory, we offer comprehensive Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) services to provide full workflow solutions, from DNA isolation and sequencing to advanced bioinformatic analyses for ready-to-publish data. Our experienced staff have extensive expertise working with a variety of environmental and human sample types, including stool, saliva, soil, water and more. We are here to help!

Our NGS Clients
We are pleased to work with some of the most prestigious companies and institutions in 155+ countries.
Bioinformatics Analysis
Your Custom Workflow
1. Consultation
2. Sample Submission/Shipping
3. Sample Isolation
4. DNA Quality Control
5. Library Preparation
6. Sequencing
7. Bioinformatics Analysis
8. Final Report
Step 1: Consultation
Get started by requesting your free consultation with one of our metagenomics experts. We would love to discuss your research objectives and are happy to provide assistance in defining your project goals. Our NGS specialists and bioinformaticians are here to provide customized recommendations to suit your project needs.
Request Your Consultation
Step 2: Sample Submission & Shipping
Shipping your samples to our facility is easy and painless! We’ll provide you with detailed instructions on how to handle, process and ship your samples to our laboratory. We accept both purified DNA and specimens for DNA isolation services.
If you are shipping specimens to us, a complete guide on sample collection and preservation will be provided to you. Recommended specimen input and handling procedures for DNA purification can be found in our Metagenomics Service Guide.
How will you submit your samples?
For detailed shipping instructions, please refer to the document below.
Shipping Instructions
Step 3: Sample Isolation
DNA isolation is included in your 16S rRNA. With tremendous experience and expertise in isolating DNA from various sample types, our NGS team can work with even the most challenging samples.

Step 4: DNA Quality Control
You can be confident that the sequencing portion of your project will be successful as we perform quality control on the isolated DNA to assess quantity, quality, and amplifiability prior to library preparation.

Step 5: Library Preparation
Norgen offers 16S Metagenomics Sequencing for any of the 9 target regions of the 16S gene. Based on the target region of your choice, we generate DNA libraries using Norgen Biotek’s Metagenomics Library Prep Kits. The DNA library will then undergo a quality check prior to sequencing.

Step 6: Sequencing
We will sequence your libraries on the Illumina MiSeq platform to achieve your required coverage and read depth.

Step 7: Bioinformatics Analysis
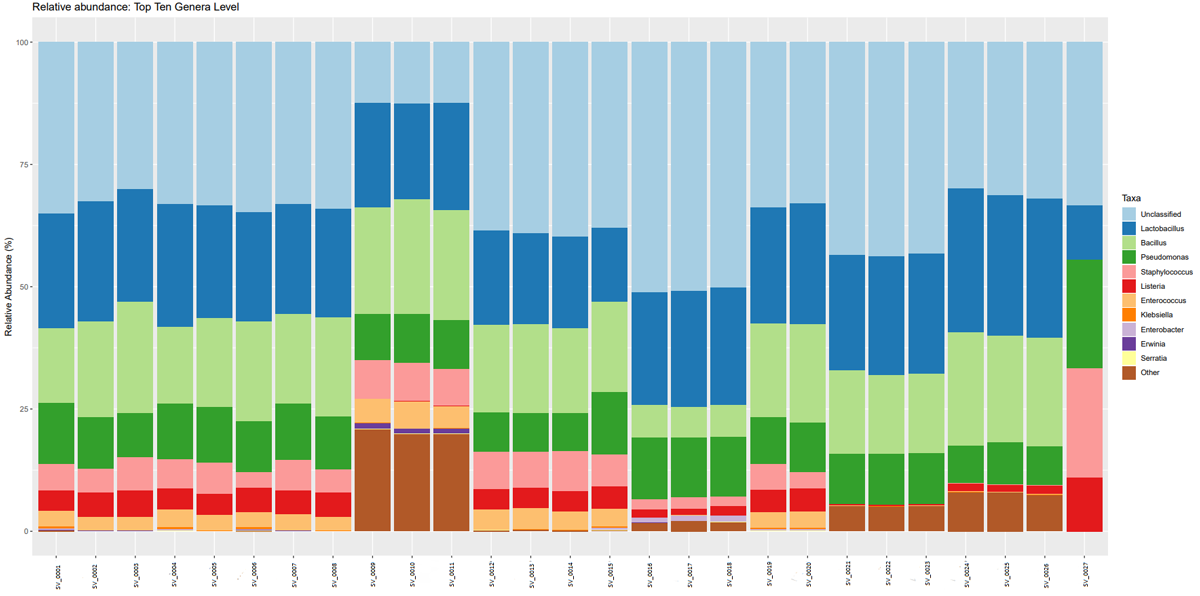
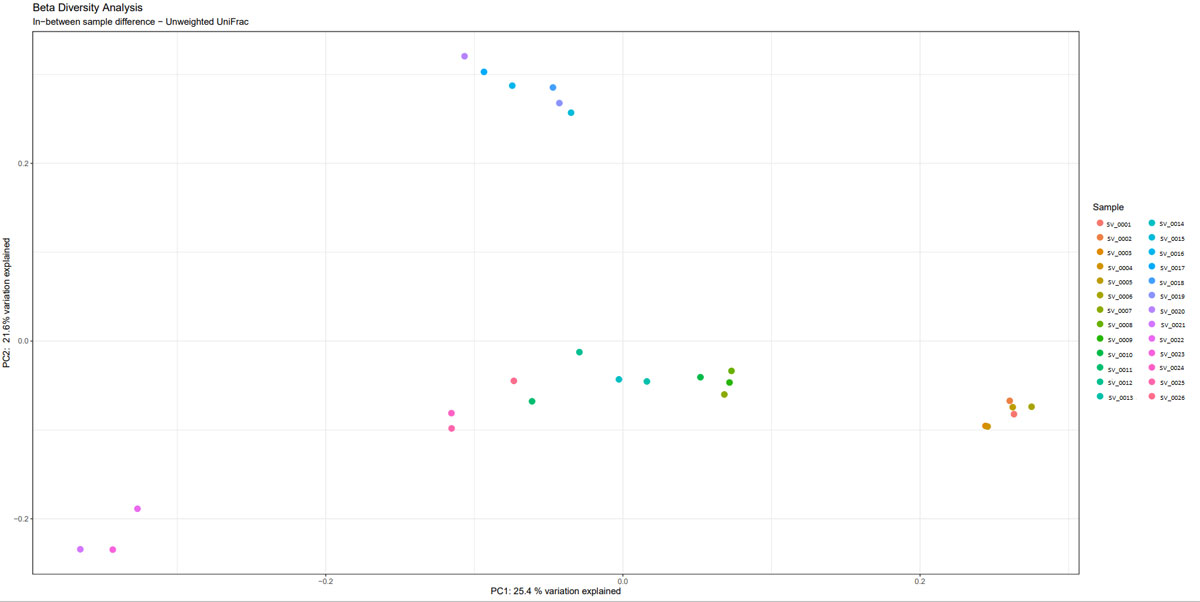
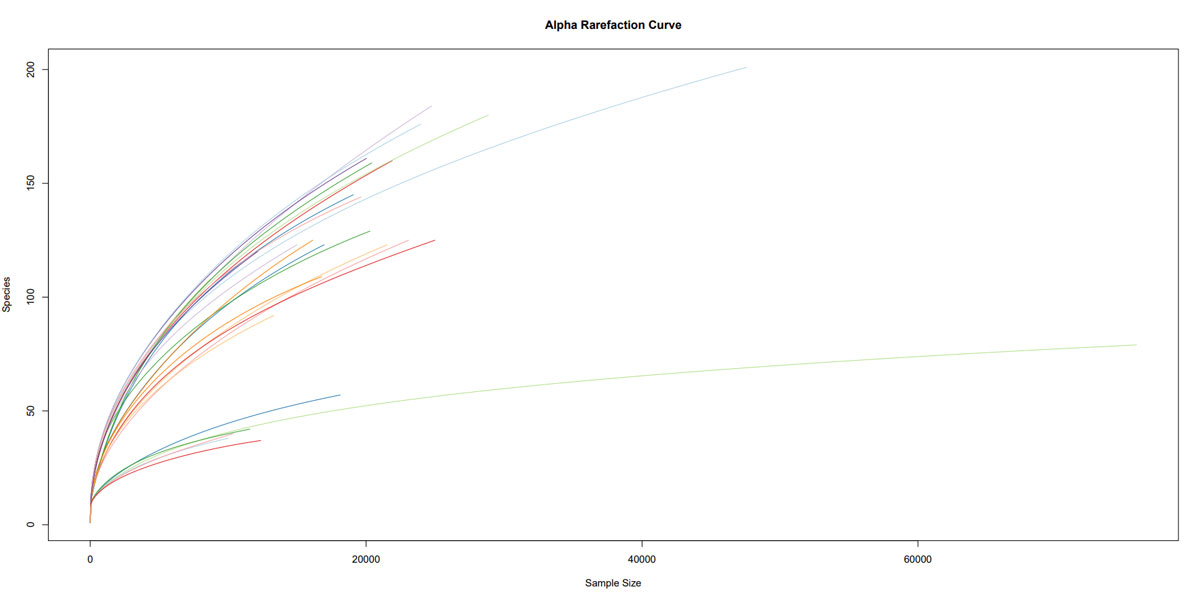
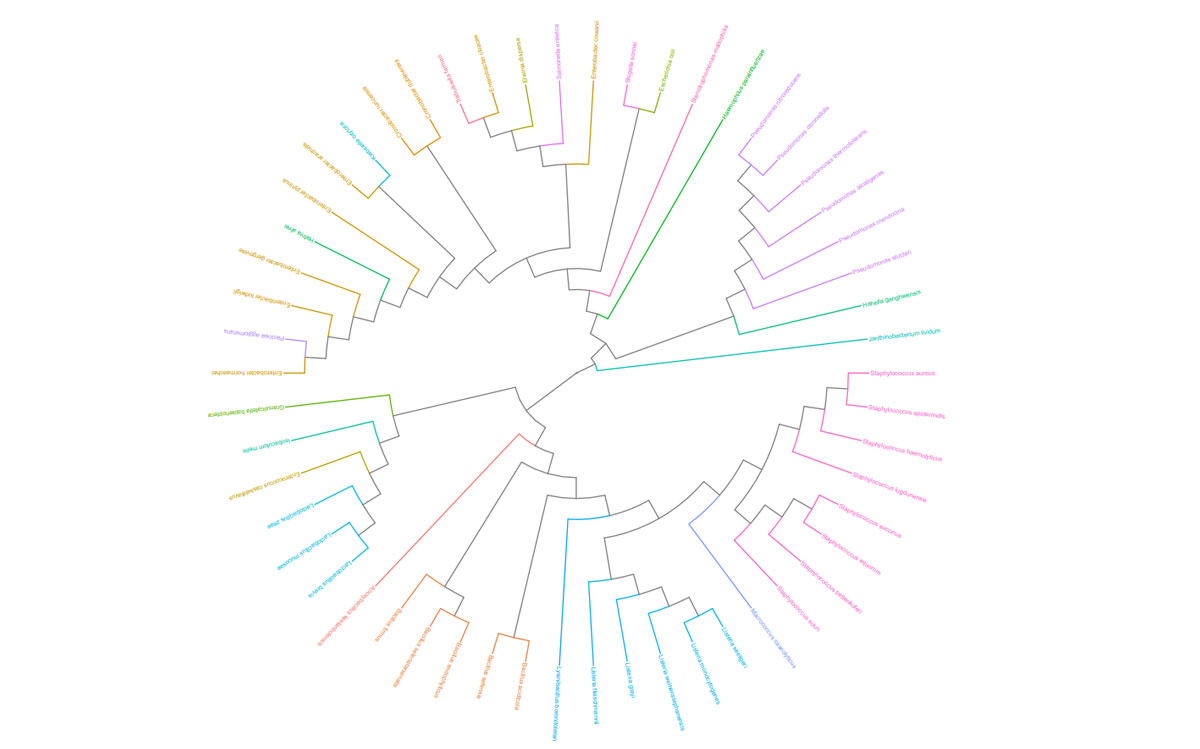
Once the sequencing is complete, our team of bioinformaticians conduct a comprehensive analysis to help make sense of your data. The analysis includes taxonomic classification down to the phylum and genus level, Shannon diversity index, OTU (operational taxonomic unit) classification with 97% similarity identity, weighted and unweighted diversity and rooted phylogenetic relationships. You will receive a final report, which will include a summary of your project as well as your data illustrated in ready-to-publish figures.
Sample Report
Let's get your project started.
Request Your Consultation16S Variable Region Interactive Tool
Using the Interactive Variable Region Diagram, select any of the regions below to learn about which variable region may be best suited for your sequencing project.
Region V1 to V2 (Nucleotides 69-242)
- Used to distinguish Streptococcus sp. and differentiate between Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase negative Staphylococcus species
- Able to distinguish among Staphylococcal, Streptococcal, Clostridium, Haemophilus and Neisseria species
- Best target for distinguishing among Mycobacterium sp.
- Able to detect Actinomycetaceae, Bacillaceae, Bacteriodaceae, Clostridiaceae, Deinococcaceae, Enterococcaceae, Helicobacteraceae, Lactobacillaceae, Listeriaceae, Moraxellaceae, Neisseriaceae, Propionibacteriaceae, Pseudomonadaceae, Rhodobacteraceae, Staphylococcaceae, Streptococcaceae at both the Family and Genus level
- Able to detect Enterobacteriaceae at the Family level only
- Not useful for most Escherichia sp., Shigella sp., K. pneumoniae and E. aerogene
Region V1 to V3 (Nucleotides 69-497)
- Used to distinguish Staphylococci populations
- Able to detect Prevotella, Porphyromonas, and Bacteroides
Region V1 to V2 (Nucleotides 69-242)
- Used to distinguish Streptococcus sp. and differentiate between Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase negative Staphylococcus species
- Able to distinguish among Staphylococcal, Streptococcal, Clostridium, Haemophilus and Neisseria species
- Best target for distinguishing among Mycobacterium sp.
- Able to detect Actinomycetaceae, Bacillaceae, Bacteriodaceae, Clostridiaceae, Deinococcaceae, Enterococcaceae, Helicobacteraceae, Lactobacillaceae, Listeriaceae, Moraxellaceae, Neisseriaceae, Propionibacteriaceae, Pseudomonadaceae, Rhodobacteraceae, Staphylococcaceae, Streptococcaceae at both the Family and Genus level
- Able to detect Enterobacteriaceae at the Family level only
- Not useful for most Escherichia sp., Shigella sp., K. pneumoniae and E. aerogene
Region V1 to V3 (Nucleotides 69-497)
- Used to distinguish Staphylococci populations
- Able to detect Prevotella, Porphyromonas, and Bacteroides
Region V1 to V2 (Nucleotides 69-242)
- Used to distinguish Streptococcus sp. and differentiate between Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase negative Staphylococcus species
- Able to distinguish among Staphylococcal, Streptococcal, Clostridium, Haemophilus and Neisseria species
- Best target for distinguishing among Mycobacterium sp.
- Able to detect Actinomycetaceae, Bacillaceae, Bacteriodaceae, Clostridiaceae, Deinococcaceae, Enterococcaceae, Helicobacteraceae, Lactobacillaceae, Listeriaceae, Moraxellaceae, Neisseriaceae, Propionibacteriaceae, Pseudomonadaceae, Rhodobacteraceae, Staphylococcaceae, Streptococcaceae at both the Family and Genus level
- Able to detect Enterobacteriaceae at the Family level only
- Not useful for most Escherichia sp., Shigella sp., K. pneumoniae and E. aerogene
Region V2 to V3 (Nucleotides 137-497)
- Targets speciation among Staphylococcal and Streptococcal pathogens as well as Clostridium and Niesseria, Mycobacterium, and Haemophilius
Region V1 to V3 (Nucleotides 69-497)
- Used to distinguish Staphylococci populations
- Able to detect Prevotella, Porphyromonas, and Bacteroides
Region V2 to V3 (Nucleotides 137-497)
- Targets speciation among Staphylococcal and Streptococcal pathogens as well as Clostridium and Niesseria, Mycobacterium, and Haemophilius
Region V1 to V3 (Nucleotides 69-497)
- Used to distinguish Staphylococci populations
- Able to detect Prevotella, Porphyromonas, and Bacteroides
Region V2 to V3 (Nucleotides 137-497)
- Targets speciation among Staphylococcal and Streptococcal pathogens as well as Clostridium and Niesseria, Mycobacterium, and Haemophilius
Region V3 to V4 (Nucleotides 433-682)
- Better than region V2 in distinguishing between enterobacteriaceae K. pneumoniae and E. aerogenes
- Able to detect Actinomycetaceae, Bacillaceae, Bacteroidaceae, Clostridiaceae, Enterococcaceae, Lactobacillaceae, Listeriaceae, Moraxellaceae, Neisseriaceae, Pseudomonadaceae, Staphylococcaceae, Streptococcaceae at both the Family and Genus level
- Able to detect Enterobacteriaceae at the Family level only
Region V1 to V3 (Nucleotides 69-497)
- Used to distinguish Staphylococci populations
- Able to detect Prevotella, Porphyromonas, and Bacteroides
Region V3 to V5 (Nucleotides 433-879)
- Able to detect Coxiellaceae, Enterococcaceae, and unclassified families within Firmicutes amd Tenericutes
Region V3 to V4 (Nucleotides 433-682)
- Better than region V2 in distinguishing between enterobacteriaceae K. pneumoniae and E. aerogenes
- Able to detect Actinomycetaceae, Bacillaceae, Bacteroidaceae, Clostridiaceae, Enterococcaceae, Lactobacillaceae, Listeriaceae, Moraxellaceae, Neisseriaceae, Pseudomonadaceae, Staphylococcaceae, Streptococcaceae at both the Family and Genus level
- Able to detect Enterobacteriaceae at the Family level only
Region V3 to V5 (Nucleotides 433-879)
- Able to detect Coxiellaceae, Enterococcaceae, and unclassified families within Firmicutes amd Tenericutes
Region V4 (Nucleotides 576-682)
- Able to detect Actinomycetaceae, Bacillaceae, Bacteriodaceae, Clostridiaceae, Deinococcaceae, Enterococcaceae, Helicobacteraceae, Lactobacillaceae, Listeriaceae, Moraxellaceae, Propionibacteriaceae, Rhodobacteraceae, Staphylococcaceae, Streptococcaceae at both the Family and Genus level
- Able to detect Enterobacteriaceae, Neisseriaceae, Pseudomonadaceae at the Family level only
Region V3 to V4 (Nucleotides 433-682)
- Better than region V2 in distinguishing between enterobacteriaceae K. pneumoniae and E. aerogenes
- Able to detect Actinomycetaceae, Bacillaceae, Bacteroidaceae, Clostridiaceae, Enterococcaceae, Lactobacillaceae, Listeriaceae, Moraxellaceae, Neisseriaceae, Pseudomonadaceae, Staphylococcaceae, Streptococcaceae at both the Family and Genus level
- Able to detect Enterobacteriaceae at the Family level only
Region V4 to V5 (Nucleotides 576-879)
- Able to detect P. acnes and B. cepacia
Region V3 to V5 (Nucleotides 433-879)
- Able to detect Coxiellaceae, Enterococcaceae, and unclassified families within Firmicutes amd Tenericutes
Region V4 to V5 (Nucleotides 576-879)
- Able to detect P. acnes and B. cepacia
Region V3 to V5 (Nucleotides 433-879)
- Able to detect Coxiellaceae, Enterococcaceae, and unclassified families within Firmicutes amd Tenericutes
Region V4 to V5 (Nucleotides 576-879)
- Able to detect P. acnes and B. cepacia
Region V3 to V5 (Nucleotides 433-879)
- Able to detect Coxiellaceae, Enterococcaceae, and unclassified families within Firmicutes amd Tenericutes
Region V5 to V7 (Nucleotides 822-1173)
- Able to detect Cyanobacteria and picocyanobacterial communities, such as Synechococcus, Prochlorococcus, and Cyanobium
Region V5 to V7 (Nucleotides 822-1173)
- Able to detect Cyanobacteria and picocyanobacterial communities, such as Synechococcus, Prochlorococcus, and Cyanobium
Region V5 to V7 (Nucleotides 822-1173)
- Able to detect Cyanobacteria and picocyanobacterial communities, such as Synechococcus, Prochlorococcus, and Cyanobium
Region V5 to V7 (Nucleotides 822-1173)
- Able to detect Cyanobacteria and picocyanobacterial communities, such as Synechococcus, Prochlorococcus, and Cyanobium
Region V5 to V7 (Nucleotides 822-1173)
- Able to detect Cyanobacteria and picocyanobacterial communities, such as Synechococcus, Prochlorococcus, and Cyanobium
Region V7 to V9 (Nucleotides 1117-1465)
- Able to detect Veillonella populations
- Able to detect Deinococcaceae, Moraxellaceae, and Streptococcaceae at both the Family and Genus level
- Able to detect Enterobacteriaceae at Family level only
Region V7 to V9 (Nucleotides 1117-1465)
- Able to detect Veillonella populations
- Able to detect Deinococcaceae, Moraxellaceae, and Streptococcaceae at both the Family and Genus level
- Able to detect Enterobacteriaceae at Family level only
Region V7 to V9 (Nucleotides 1117-1465)
- Able to detect Veillonella populations
- Able to detect Deinococcaceae, Moraxellaceae, and Streptococcaceae at both the Family and Genus level
- Able to detect Enterobacteriaceae at Family level only
Quality In → Quality Out
We believe that the best research starts with quality sample collection and preservation.
 Saliva DNA Collection and Preservation Devices Dx
(Cat. 49000)
Saliva DNA Collection and Preservation Devices Dx
(Cat. 49000) CE-IVD marked in accordance with EU Directive 98/79/EC
 Total Nucleic Acid Preservation Tubes Dx
(Cat. Dx69200)
Total Nucleic Acid Preservation Tubes Dx
(Cat. Dx69200) CE-IVD marked in accordance with EU Directive 98/79/EC
 Swab Collection and DNA Preservation System
(Cat. 45690-B)
Swab Collection and DNA Preservation System
(Cat. 45690-B) For Research Use
 Stool Nucleic Acid Collection and Preservation Devices Dx
(Cat. Dx45660)
Stool Nucleic Acid Collection and Preservation Devices Dx
(Cat. Dx45660) CE-IVD marked in accordance with EU Directive 98/79/EC
 Stool Nucleic Acid Collection and Preservation System
(Cat. 63700)
Stool Nucleic Acid Collection and Preservation System
(Cat. 63700) For Research Use
 Fecal DNA Collection & Preservation Mini Tubes
(Cat. 27650)
Fecal DNA Collection & Preservation Mini Tubes
(Cat. 27650) For Research Use
 Fecal Swab Collection and Preservation System
(Cat. 45670)
Fecal Swab Collection and Preservation System
(Cat. 45670) For Research Use
 Urine Preservation
(Cat. 18116, 18118, 18120)
Urine Preservation
(Cat. 18116, 18118, 18120) For Research Use
 Urine Collection and Preservation Cup
(Cat. 18129)
Urine Collection and Preservation Cup
(Cat. 18129) For Research Use
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Next Generation Sequencing?
Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) is an important tool used in the field of genomic research as it allows for high throughput and massively parallel sequencing of thousands of molecules simultaneously. NGS provides researchers with fast, scalable solutions for a clear, complete picture of their samples to advance their scientific discoveries.
What is bioinformatics?
Bioinformatics has quickly advanced to become an important and powerful application in biological research. It involves a combination of computational and statistical methods to better understand and analyze scientific data, guiding the research community to new opportunities and novel discoveries. As an emerging discipline, bioinformatics continues to be an essential tool for researchers in many fields including modern molecular biology and clinical research, with its applications leading to significant medical advancements and developments in future research to come.
Why should I choose Norgen for my microbiome sequencing?
Norgen Biotek is an ISO-certified state-of-the-art laboratory specializing in Next Generation Sequencing using the Illumina platform. We provide comprehensive solutions for a wide range of applications including healthcare, agriculture and environmental monitoring. Our expert scientists have vast experience with challenging sample types and we strive to ensure we support our customers at every stage of their project. We pride ourselves on providing our customers with quality data to accelerate their research in microbiome advancements.
Do you offer extraction services?
Yes. Our comprehensive 16S rRNA Sequencing service includes DNA extraction and QC from any sample type.
What are your sample submission requirements?
Our requirements for sample submission can be found under Step 2: Sample Submission on our Metagenomics NGS Service page.
What amplicon regions do you sequence?
We offer 9 primers which target the 9 regions of the 16S rRNA gene. Ranging from V1-V9, each target has a specificity to certain bacterial profiles. For instance, the commonly used V3-V4 region is great for detecting most bacteria at a genus level. If you aren’t sure which region is best for your samples, you can use our interactive Variable Region Diagram, or you can always consult with us and our NGS scientists would be happy to make a recommendation.
What sequencing platform do you sequence on?
We sequence all 16S Metagenomics Sequencing projects on the Illumina MiSeq platform.
What is the depth of coverage Norgen provides?
Norgen’s standard 16S rRNA Sequencing service provides an average of 50K* raw reads per sample. * May differ for low biomass samples. Please contact services@norgenbiotek.com for our recommendations if you are working with low biomass samples.
Does the price include bioinformatics analysis?
Yes. Our comprehensive service includes a full bioinformatics analysis of your raw data. We deliver the bioinformatics analysis in a PDF report and we also provide you with a secure link to download all of your raw data and intermediate files.
What is the typical turnaround time?
Our typical turnaround time is 3-4 weeks from the time of sample receipt. The turnaround time is dependent on the size of your project. Please contact services@norgenbiotek.com to receive an accurate estimated turnaround time.
Norgen is located in Canada. Do you still accept samples from other countries?
Absolutely! We accept samples from countries worldwide and our NGS team will be happy to assist you with making the shipping arrangements.
Citations
| Title | Effects of a 10-Strain Oral Probiotic on Parameters of Vaginal Health and Microbial Community: A Pilot Clinical Study |
| Journal | Int J Womens Health. 2022. |
| Authors | Christopher J Martoni, Amalie Kruse Sigersted Frederiksen, Anders Damholt, and Gregory Leyer |
| Title | Characterization of the urogenital microbiome in Miniature Schnauzers with and without calcium oxalate urolithiasis |
| Journal | Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine. 2022. |
| Authors | Emily L. Coffey, Andres M. Gomez, Erin N. Burton, Jennifer L. Granick, Jody P. Lulich, Eva Furrow |