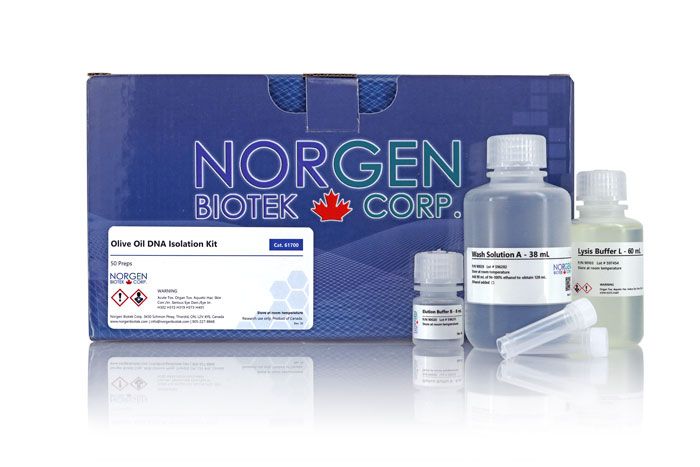
Olive Oil DNA Isolation Kit
For the rapid preparation of genomic DNA from olive oil
For research use only and NOT intended for in vitro diagnostics.
Olive Oil DNA Isolation Kit
For the rapid preparation of genomic DNA from olive oil
Register today to receive an exclusive 15% off* on your first order.
Features and Benefits
- Fast and easy processing using a rapid spin-column format
- Isolate total DNA without compromising total yield
- No phenol or chloroform extractions
- Isolate high quality total DNA from a variety of oil samples in order to support genetic traceability by allowing for the verification of the authenticity of the oil, thereby discouraging adulteration
Norgen’s Olive Oil DNA Isolation Kit is designed for the rapid preparation of genomic DNA from olive oil in order to support genetic traceability by allowing for the verification of the authenticity of the oil, thereby discouraging adulteration. Norgen’s Olive Oil DNA Isolation Kit can also be used to purify DNA from other processed oils such as canola oil, sunflower oil or vegetable oil to allow for downstream analysis and testing for oil adulteration. Genomic DNA is efficiently extracted from 0.5 mL of oil by a combination of heat treatment, homogenization and a unique lysis buffer. PCR inhibitors are effectively removed during the washing steps and the purified genomic DNA is ready to use for downstream applications such as PCR and microarray analysis. Preparation time for ten samples is less then 30 minutes, and each kit contains sufficient materials for 50 preparations.
Details
Supporting Data
Figure 1. Process a Variety of Different Food Oils. A variety of different food oils purchased from stores can be processed for DNA isolation using Norgen's Olive Oil DNA Isolation Kit. The high quality of the purified DNA is shown in the Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA (RAPD) analysis (See Figure 2).
Figure 2. Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA (RAPD) Analysis of 10 Food Oil Products. Inputs of 0.5 mL of oil were processed using Norgen’s Olive Oil DNA Isolation Kit, and 5 µL of the 40 µL eluted DNA was used in 20 µL of RAPD reaction. The RAPD pattern indicates successful RAPD amplification with high DNA quality. Ma: Norgen’s UltraRanger 1 kb DNA Ladder (Cat. 12100), Mb: HighRanger 1 kb DNA Ladder (Cat. 11900).
|
Kit Specifications
|
|
|
Maximum Column Binding Capacity
|
10 µg
|
|
Maximum Column Loading Volumes
|
650 µL
|
| Time to Complete 10 Purifications |
25 minutes
|
Storage Conditions and Product Stability
All solutions should be kept tightly sealed and stored at room temperature. This kit is stable for 1 year after the date of shipment.
Component | Cat. 61700 (50 preps) |
|---|---|
Lysis Buffer L | 60 mL |
Binding Buffer B | 40 mL |
Wash Solution A | 38 mL |
Elution Buffer B | 8 mL |
Homogenization Tubes | 50 |
Spin Columns | 50 |
Collection Tubes | 50 |
Elution Tubes (1.7 mL) | 50 |
Product Insert | 1 |
Documentation
FAQs
Spin Column
Clogged columns may occur due to improper oil removal. Too much oil was carried over to the lysate. Repeat Step 1d and 1e to minimize the oil carry over. Clogging can be alleviated by increasing the g-force and/or centrifuging for a longer period of time until the lysate passes through the column.
If the DNA does not perform well in downstream applications, it may be due to one or more of the following:
- Low DNA yield.
Depending on the oil extraction process, DNA can be damaged or lost. Increase the input volume up to 1 mL, as well as the other buffers and solutions proportionally.
- Ethanol carryover.
Ensure that the dry spin under the Column Wash procedure is performed in order to remove traces of ethanol prior to elution. Ethanol is known to interfere with many downstream applications.
- The column was not washed twice with the provided Wash Solution A.
Traces of salt from the binding step may remain in the sample if the column is not washed twice with Wash Solution A. Salt may interfere with downstream applications, and thus must be washed from the column.
- PCR reaction conditions need to be optimized.
Take steps to optimize the PCR conditions being used, including varying the amount of template (20 ng to 50 ng for 20 µL of PCR reaction), changing the source of Taq polymerase, adding BSA (final concentration is 0.1 µg/µL), looking into the primer design, and adjusting the annealing conditions.
The yield varies a lot with the variety and processing status of the olive oil.
Citations
| Title | Multiallelic DNA sensors for molecular traceability of olive oil varietal origin |
| Citation | Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 2024. |
| Authors | Natalia-Maria Christopoulou a, Eleftheria Figgou b, Panagiotis Kalaitzis b, Despina P. Kalogianni a, Theodore K. Christopoulos a c |
| Title | Screening Method for the Visual Discrimination of Olive Oil from Other Vegetable Oils by a Multispecies DNA Sensor |
| Citation | Analytical Chemistry 2024. |
| Authors | Natalia-Maria Christopoulou, Vasiliki Mamoulaki, Aglaia Mitsiakou, Eleni Samolada, Despina P. Kalogianni*, and Theodore K. Christopoulos* |
| Title | A modified isooctane-based DNA extraction method from crude oil |
| Citation | mLife 2023. |
| Authors | Armando Alibrandi, Rolando di Primio, Alexander Bartholomäus, Jens Kallmeyer |