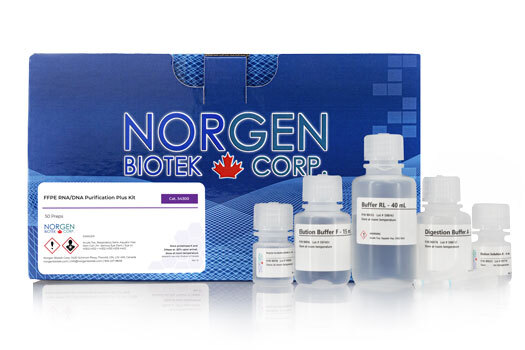
FFPE RNA/DNA Purification Plus Kit Dx
Sequential isolation and purification of total RNA and genomic DNA from FFPE tissue samples

Intended for in vitro diagnostics use.
Research version available here
This product is not available for purchase in the United States.
FFPE RNA/DNA Purification Plus Kit Dx
Sequential isolation and purification of total RNA and genomic DNA from FFPE tissue samples
Register today to receive an exclusive 15% off* on your first order.
Features and Benefits
- Fast and easy processing using rapid spin-column format
- High yields and quality of nucleic acids
- Separate fractionation of RNA and DNA
- Isolate total RNA, from large rRNA down to microRNA (miRNA)
- No phenol or chloroform extractions
- Purified RNA is suitable for a variety of downstream applications, including Small RNA Sequencing. Find out more information on Norgen's NGS services
- Purification is based on spin column chromatography that uses Norgen’s proprietary resin separation matrix
Norgen’s FFPE RNA/DNA Purification Plus Kit Dx provides a rapid method for the sequential isolation and purification of total RNA (including microRNA) and genomic DNA from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue samples for subsequent in vitro diagnostic use. Using formalin to fix tissues leads to crosslinking of the nucleic acids and proteins, and the process of embedding the tissue samples can also lead to fragmentation of the nucleic acids over time. Norgen’s FFPE RNA/DNA Purification Plus Kit Dx provides conditions that allow for the partial reversing of the formalin modifications, resulting in a high quality and yield of nucleic acids. The kit is able to purify all sizes of RNA, from large mRNA and ribosomal RNA down to microRNA (miRNA) and small interfering RNA (siRNA), depending on the age of the FFPE tissue as the degree of fragmentation of the RNA will increase over time.
This kit is designed to be used with any downstream application employing enzymatic amplification or other enzymatic modifications of nucleic acids followed by signal detection or amplification. Any diagnostic results generated using the RNA and DNA isolated with Norgen’s FFPE RNA/DNA Purification Plus Kit Dx in conjunction with an in vitro diagnostic assay should be interpreted with regard to other clinical or laboratory findings.
To minimize irregularities in diagnostic results, suitable controls for downstream applications should be used.
Norgen’s FFPE RNA/DNA Purification Plus Kit Dx is intended for use by professional users such as technicians, physicians and biologists experienced and trained in molecular biological techniques.
Norgen’s FFPE RNA/DNA Purification Plus Kit Dx does not provide a diagnostic result. It is the sole responsibility of the user to use and validate the kit in conjunction with a downstream in vitro diagnostic assay.
Details
Supporting Data
Figure 1. Superior Recovery of High Quality RNA and DNA from FFPE Spleen Tissues. Norgen's FFPE RNA/DNA Purification Plus Kit Dx isolates FFPE RNA and DNA that exceeds the yield of competitors. Total RNA and DNA was isolated from equal amount of hamster FFPE spleen sections (20 micron thickness) using Norgen's FFPE RNA /DNA Purification Plus Kit Dx and a leading competitor’s kits. Triplicate isolations were performed for each product. The top graphs demonstrate the mean yield of RNA (Panel A) and DNA (Panel B) according to NanoDrop measurement. The bottom graphs showed the mean 260:280 ratio and 260:230 ratio of RNA (Panel C) and DNA (Panel D) according to NanoDrop measurement. Norgen's kit consistently purified total RNA and DNA with a higher yield and higher quality than for those obtained using the market competitor's kits.
Figure 2. Recovery of High Quality DNA and True Total RNA including microRNA from Hamster Spleen. Genomic DNA isolated using Norgen's FFPE RNA/DNA Purification Plus Kit Dx is of high quality with effective qPCR amplification. Panel A showed that in a qPCR using primers against the 5S rRNA gene using equal amount of FFPE DNA as template, the DNA isolated with Norgen's kit showed better amplification (lower Ct value). Moreover, Norgen's FFPE RNA/DNA Purification Plus Kit isolates true total RNA including microRNA. With the same amount of RNA as template in RT-qPCR reactions for transcripts of miR-21 (Panel B for microRNA) and beta-Actin (Panel C for mRNA), RNA isolated by Norgen showed better amplification in beta-Actin and significantly better in miR-21 microRNA.
|
Kit Specifications
|
|
|
Maximum Column Binding Capacity (RNA)
|
35 μg
|
|
Maximum Column Binding Capacity (gDNA)
|
10 μg
|
|
Maximum Column Loading Volume
|
600 μL
|
|
Size of RNA Purified
|
All sizes, including small RNA (< 200 nt) |
| Maximum Amount of Starting Material |
4 sections <20 μM thick
10 mg of unsectioned block |
Storage Conditions and Product Stability
The DNAse I and Proteinase K should be stored at -20°C upon arrival. All other solutions and kit components should be kept tightly sealed and stored at room temperature. All solutions and plastics can be used until the expiration date specified on their labels.
| Component | Cat. 54300 (50 preps) |
|---|---|
| Digestion Buffer | 2 x 20 mL |
| Binding Solution | 2 x 20 mL |
| Enzyme Incubation Buffer A | 6 mL |
| RNA Wash Solution | 24 mL |
| DNA Wash Solution | 38 mL |
| RNA Elution Solution | 6 mL |
| DNA Elution Buffer | 15 mL |
| Proteinase K | 2 x 12 mg |
| DNase I | 200 μL |
| RNA Purification Micro Columns | 50 |
| DNA Purification Micro Columns | 50 |
| Collection Tubes | 100 |
| Elution Tubes (1.7 mL) | 100 |
| Product Insert | 1 |
Documentation
Citations
| Title | The use of whole genome methylation scanning to define genes preferentially suppressed in African American Prostate Cancer |
| Journal | Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers and Prevention. 2017. |
| Authors | Farah Rahmatpanah, Kathleen McGuire, Michael Lilly, Michael McClelland and Dan Mercola |
| Title | MicroRNA-34c-5p is related to recurrence in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma |
| Journal | The Laryngoscope. 2015. |
| Authors | Massimo Re MD, Artan Çeka MD, Corrado Rubini MD, Luigi Ferrante PhD, Antonio Zizzi PhD, Federico M. Gioacchini MD, Michele Tulli MD, Liana Spazzafumo PhD, Stefano Sellari-Franceschini MD, Antonio D. Procopio MD, andFabiola Olivieri PhD |
| Title | In-Vivo Fusion of Human Cancer and Hamster Stromal Cells Permanently Transduces and Transcribes Human DNA |
| Journal | PLOS ONE. 2014. |
| Authors | David M. Goldenberg, Robert J. Rooney, Meiyu Loo, Donglin Liu, Chien-Hsing Chang |
| Title | The miRNA-23b/27b/24 Cluster Promotes Breast Cancer Lung Metastasis by Targeting Metastasis-Suppressive Gene Prosaposin. |
| Journal | The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2014. |
| Authors | Brian Ell, Qiong Qiu, Yong Wei, Laura Mercatali, Toni Ibrahim, Dino Amadori and Yibin Kang |
| Title | Tumor-Induced Osteoclast miRNA Changes as Regulators and Biomarkers of Osteolytic Bone Metastasis. |
| Journal | Cancer Cell. 2013. |
| Authors | Ell B, Mercatali L, Ibrahim T, Campbell N, Schwarzenbach H, Pantel K, Amadori D, Kang Y. |
| Title | Tyrosine kinase receptor status in endometrial stromal sarcoma: an immunohistochemical and genetic-molecular analysis. |
| Journal | International Journal of Gynecology Pathology. 2012. |
| Authors | Cossu-Rocca P, Contini M, Uras MG, Muroni MR, Pili F, Carru C, Bosincu L, Massarelli G, Nogales FF, De Miglio MR. |
| Title | Factors affecting the yield of microRNAs from laser microdissectates of formalin-fixed tissue sections. |
| Journal | BMC Research Notes. 2012. |
| Authors | Patnaik SK, Kannisto E, Yendamuri S. |
| Title | Overexpression of the Lung Cancer-Prognostic miR-146b MicroRNAs Has a Minimal and Negative Effect on the Malignant Phenotype of A549 Lung Cancer Cells. |
| Journal | PLoS One. 2011. |
| Authors | Patnaik S, Kannisto E, Mallick R, Yendamuri S. |